1. The SCRUM agile method
-
Scrum is an agile process dedicated to produce the most client value in the shortest time.
-
Working software is produced on every iteration (sprint)
-
The client provides priorities.
-
The team self-organize itself to better match client priorities
-
At the end of every sprint, everybody can check that the product runs (or not) and decide to deliver a release or not.
1.1. SCRUM roles
The actors in Scrum are:
- The Product Owner
-
the client or its representative, who is part of the team
- The SCRUM Master
-
an animator, not a manager
- The Team
-
everybody else, without specific role
1.1.1. Product Owner
-
Define and is responsible of the product’s features
-
Choose the dates and content of the releases
-
Is responsible of the ROI return on investment
-
Define priorities in the product backlog
-
Ajust features and priorities at each sprint (if necessary)
-
Accept or reject results
1.1.2. SCRUM Master
-
Ensure the sustainability of the project
-
Help applying Scrum values and practices
-
Help resolving problems and fight impediments
-
Ensure that the team is fully functionnal and productive
-
Facilitate cooperation between team members
-
Protect the team from outside "noise"
1.1.3. SCRUM Team
-
5 to 10 people, preferably fully dedicated to the project only
-
All roles and specialities together Architecture, design, coding, GIU, tests, etc.
-
Self-organize itself
-
Do not change during a sprint
1.2. The SCRUM process

-
Plannification of the following sprint
-
Selection of product backlog items that will be developed during the sprint
-
Definition of the tasks and of the sprint backlog
-
-
Daily SCRUM (15mn)
-
or "stand-up" meeting
-
what did I do yesterday ?
-
what will I do today ?
-
is there any particular problem ?
-
-
SPRINT review (15-30mn)
-
Presentation of the application to the team or invited people
-
team velocity measure
-
-
Retrospective meeting (15mn)
-
The team (including client) review its process
-
What went well: continued
-
What went wrong: let’s improve
-
-
Release planning
-
Define the items of the product backlog that will constitute the release(s)
-
Define the number of sprints and the dates of release
-
Done before first sprint by estimating team velocity (if unknown)
-
Updated at the end of each sprint
-
1.3. The SCRUM artifacts
- Product backlog
-
list of User Stories ordered by (client) value
- Sprint backlogs
-
list of tasks to be realized during the sprint to meet the selected features treated for this sprint
- Project burndowns
-
graphical representation of the team progress
1.3.1. Product Backlog
-
Il est fourni par le Product Owner au démarrage du projet
-
Il est une liste ordonnée d’exigences (stories) classées selon leur importance métier
-
Le classement de chaque exigence pourra être révisé à chaque revue de sprint par le Product Owner
-
Des exigences pourront être ajoutées/retirées à chaque revue de sprint par le Product Owner
1.3.2. Sprint Backlog
-
Defined during the sprint planning
-
List of tasks corresponding to the selected User Stories treated during the sprint
-
Tasks are "weighted" (most often in hours)
-
Time estimation of each task is updated at each daily SCRUM
-
The definition of these tasks is a kind of collective design
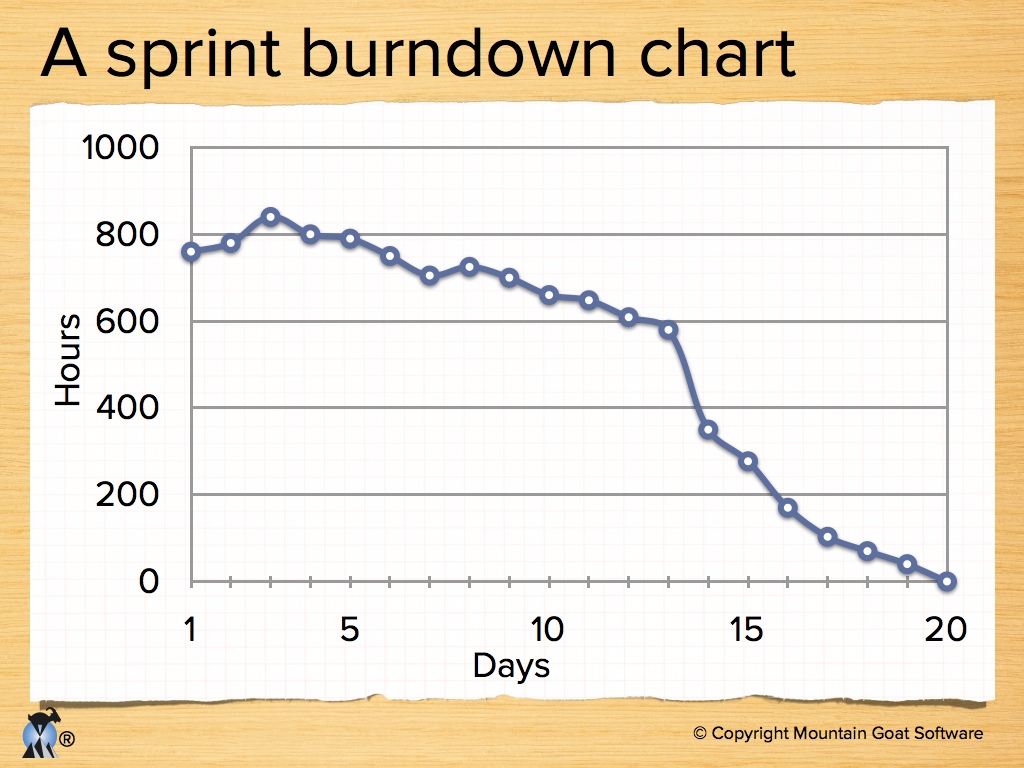
1.3.3. Project Burndowns
-
The values of the product backlog items and the estimates of the sprint backlogs allow to draw a graphical representation of the progress of the project.
Sprint Burndown
-
Updated everyday
-
Show the remaining efforts
| the sprint burndown can grow if tasks are added or re-evaluated as more costly. |
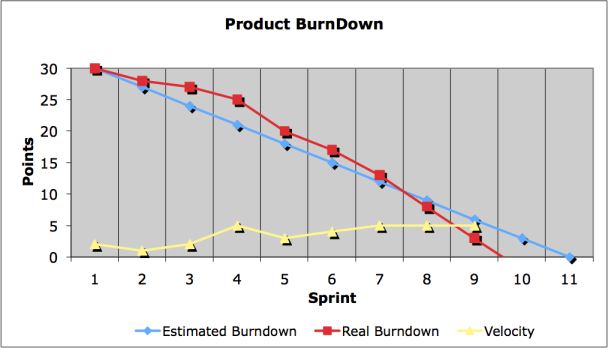
Product (or release) Burndown
-
Estimated at each end of sprint and concerns the remaining product backlog
| the release backlog is always evolving, hence the curb is not necessary going always down |
1.3.4. Indicators
- Velocity
-
quantity of the product backlog values realised by the team during the sprint
- Capacity
-
quantity of the product backlog values that will be realized at next sprint
| The name "velocity" is missleading |
Quizz
|
QUESTION
|